- Home
- About Us
- Products
- Services
- Recommendation
- Industries
- Resource
- Order Center
- Contact Us
Phenol, a compound belonging to the family of aromatic organic compounds, is an important chemical with a wide range of applications. With a chemical formula of C6H6O, phenol is characterized by a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to a benzene ring. Here, we will delve into the properties, structure, reactions, and various uses of phenol.
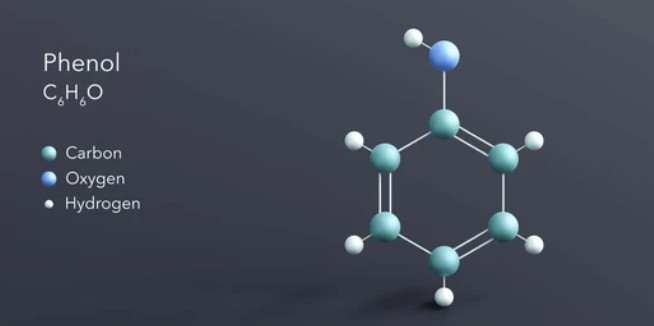
Phenol exists as a colorless crystalline solid at room temperature. It has a distinct sweet odor, which can be perceived even at low concentrations. The melting point of phenol is around 40.5 oC, and it boils at approximately 182 oC. It is sparingly soluble in water but dissolves readily in organic solvents such as ethanol, ether, and chloroform.
One of the key features of phenol is its acidity. Due to the presence of the hydroxyl group, phenol is a weak acid and readily donates a proton to a base. This acidity plays a significant role in its reactivity and chemical reactions.
Phenol is also known for its toxic properties. Its vapors can cause irritation of the respiratory tract, eyes, and skin. Prolonged exposure can lead to more severe health effects, including liver and kidney damage.
Phenol exhibits a wide range of chemical reactions, which are primarily influenced by its acidic nature and the presence of the benzene ring.
1. Acid-Base Reactions
Phenol can undergo acid-base reactions, where it acts as an acid, donating a proton (H+) to a base. This property is due to the presence of the hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to the benzene ring. For example, when phenol reacts with a strong base, such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH), the hydroxyl group of phenol donates a proton to the base, forming water and the sodium salt of phenol.
C6H5OH+NaOH→C6H5ONa+H2O
2. Esterification
Phenol can undergo esterification reactions with organic acids in the presence of an acid catalyst. This reaction involves the substitution of the hydroxyl group of phenol with an ester functional group (-COOR), resulting in the formation of an ester and water. The esterification reaction is important in the production of various phenol derivatives, such as phenyl esters used in fragrances and flavors.

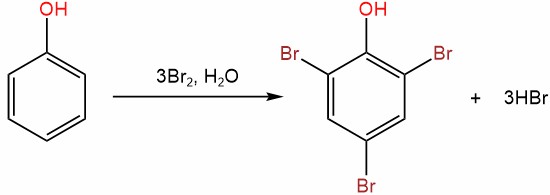
3. Halogenation
Phenol can undergo halogenation reactions where halogens, such as chlorine or bromine, replace one or more hydrogen atoms on the benzene ring. These reactions are usually carried out in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst, such as iron(III) chloride (FeCl3). The substitution of hydrogen by a halogen atom results in the formation of halophenols, which have different chemical and physical properties compared to phenol.
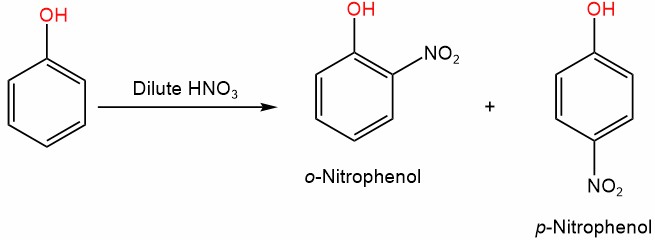
4. Nitration
Phenol can undergo nitration reactions, where a nitro group (-NO2) is introduced onto the benzene ring. This reaction is typically carried out by treating phenol with a mixture of concentrated nitric acid (HNO3) and concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4) as a catalyst. The electrophilic aromatic substitution of the nitro group changes the reactivity and properties of phenol, and nitrophenols are important intermediates in the synthesis of various chemicals, including dyes and pharmaceuticals.
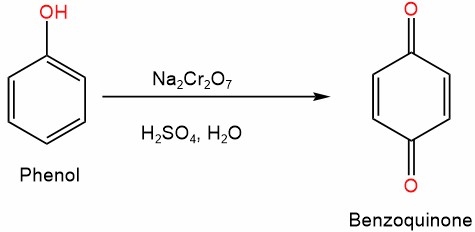
5. Oxidation
Phenol can undergo oxidation reactions, usually in the presence of an oxidizing agent, such as potassium permanganate (KMnO4) or hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Phenol can be oxidized to form quinones, which are important intermediates in the synthesis of various compounds, including pharmaceuticals and polymers.
There are numerous uses of phenol in various industries. Some of the most common uses of phenol include:
1. Chemical intermediate: Phenol is used as an intermediate in the production of various chemicals, including detergents, synthetic resins, pharmaceuticals, herbicides, and dyes.
2. Antiseptic: Phenol is an effective antiseptic and is used in the production of disinfectants, mouthwashes, and throat lozenges.
3. Personal care products: Phenol is also used in the production of personal care products, such as lotions, creams, and hair dyes.
4. Polymer production: Phenol is a vital component in the production of various polymers, including polycarbonates, epoxies, and phenolic resins.
5. Flame retardants: Phenol is used as a flame retardant in the production of materials like textiles, furniture foams, and electrical components.
6. Wood preservation: Phenol is used as a preservative for wood, helping to protect it against insects, fungi, and decay.
7. Pharmaceuticals: Phenol is used as an active ingredient in several pharmaceutical products, including topical creams for pain relief, throat sprays, and nasal sprays.
8. Animal feed additive: Phenol is sometimes used as a feed additive for livestock to enhance feed efficiency and promote growth.
9. Electronics: Phenol is used in the production of printed circuit boards and other electronic components due to its electrical insulation properties.
10. Flavoring agent: Phenol is used as a flavoring agent in certain food and beverage products, such as caramel, chocolate, and coffee.
It is important to note that phenol can be toxic and corrosive. Therefore, proper handling and safety precautions should be taken when using phenol.
Privacy Policy | Cookie Policy | Copyright © 2025 Alfa Chemistry. All rights reserved.
Back to top